Process simulation is an increasingly popular area in business process management and advanced process intelligence. In this article, we review key definitions, examples, and best practices every operations leader needs to know.
Process simulation in business operations
What is process simulation?
Process simulation is a method of analyzing and improving business processes using computer-based forecasting models. Process simulation allows businesses to explore “what if” scenarios, analyze the impact of changes to processes, and identify opportunities for improvement.
What is the goal of process simulation?
The goal of process simulation in business operations is to achieve a higher level of process efficiency, which ultimately leads to increased profitability and competitive advantage.
Process simulation is a powerful tool in process optimization because it is able to imitate different scenarios without disrupting existing operations. By creating a digital twin of a process, the simulation can be used to iterate and improve processes and adjust them to see what works best. This allows businesses to identify potential problems and opportunities for improvement before implementing them in the real world.
Why is process simulation important?
Process simulation helps identify areas of improvement in an organization’s processes. Moreover, it can be used to develop better strategies for advancing process excellence.
Process simulation can also be used to identify potential risks associated with new initiatives and to optimize existing operations as part of a process analysis project. By taking the time to analyze and simulate processes thoroughly, businesses can make better decisions and improve profitability.
Benefits of process simulation
- Risk Reduction. Before implementing changes in the real world, organizations can test them virtually, minimizing potential risks and unforeseen complications.
- Cost Efficiency. By identifying inefficiencies and testing improvements in a simulated environment, companies can avoid costly trial-and-error in real-world processes.
- Enhanced Productivity. Process simulation can pinpoint areas of underutilization, paving the way for optimal resource allocation and increased output.
- Flexibility Companies can easily test multiple scenarios, allowing for quick adjustments and agility in decision-making.
- Predictive Insights. Beyond current operations, simulations can provide valuable insights into how processes might respond to future challenges or changes.
Process simulation in 6 steps
Process simulation typically involves the following six steps:
- Process mapping. This involves creating a visual representation of the process, which includes all its steps, tasks, and decision points. This representation is often developed using flowcharts or specialized BPM software tools.
- Data gathering. Collect relevant data on the process being simulated, such as task durations, resource availability, and costs. This data is used to establish baseline performance metrics and to input realistic parameters for the simulation model.
- Model development. Create a mathematical or computational model of the process based on the process map and data gathered. This model should accurately represent the relationships between tasks, resources, and decision points within the process.
- Simulation runs. Use the model to simulate various scenarios, which may involve changing resource allocations, task durations, or process flows. This step helps to identify potential bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement.
- Analysis and optimization. Analyze the simulation results to identify trends, patterns, and opportunities for improvement. Based on the findings, adjust the process to optimize its performance, and run additional simulations to validate the proposed changes.
- Implementation and monitoring. Implement the optimized process in the real-world setting and monitor its performance to ensure that the desired outcomes are achieved. Continuous monitoring allows for ongoing adjustments as necessary, creating a cycle of continuous improvement.
How does process simulation software work?
Process simulation software uses computer algorithms and data science to create a digital model of a business process. Following that, it can forecast how the digital model would react in different kinds of process scenarios.
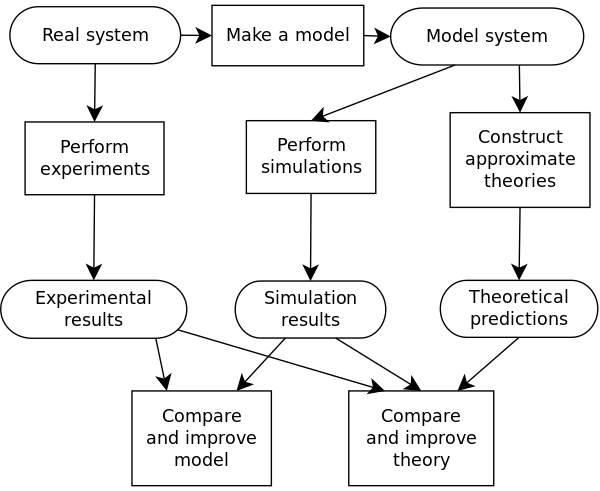
Visualization of a simulation and model. Source: Danski14 / wikipedia
By simulating different scenarios, businesses can identify bottlenecks in their processes and make changes to reduce them. This can be used to train employees on how to best use existing systems or to re-engineer new processes.
Additionally, process simulation can be used to create a digital process twin of an organization (DTO) that mimics an entire business organization in the real world.
Process simulation tools
There are several popular process simulation tools available that cater to different industries and use cases. Some of these tools are specialized for business process management, while others are more general-purpose simulation tools that can be adapted for process simulation. Here is a list of some popular process simulation tools:
- ProcessMaker: A user-friendly no-code BPM platform that provides process modeling, simulation, and automation capabilities. It supports BPMN 2.0 and uses the power of Gen AI to turn any heavy process simulation project into a quick and easy everyday task.
- Bizagi Modeler: BPM software that allows for the creation, simulation, and optimization of business processes using a simple drag-and-drop interface. It supports BPMN 2.0 standard and provides collaboration features for teams.
- Bonita: An open-source BPM software that offers process modeling, simulation, and automation features. It supports BPMN 2.0 and provides an integrated development environment for designing and deploying custom applications.
- ARIS (Architecture of Integrated Information Systems): A comprehensive BPM suite that offers process modeling, simulation, and optimization features, along with process governance and risk management capabilities. ARIS supports BPMN 2.0 and other industry standards.
- Simul8: A general-purpose simulation tool that can be used for process simulation in various industries, such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics. It features a drag-and-drop interface, customizable objects, and built-in reporting tools.
- Arena Simulation Software: A widely-used simulation tool for business processes, particularly in manufacturing, supply chain, and service industries. It offers a wide range of modules and templates to simulate different process scenarios.
- AnyLogic: A multi-method simulation software that supports discrete events, system dynamics, and agent-based modeling, making it a versatile choice for simulating complex business processes. AnyLogic offers a rich set of libraries for different industries and applications.
- ExtendSim: A general-purpose simulation tool that supports discrete event, continuous, and discrete rate modeling. It is widely used in industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and more.
FAQs:
1. What is a process simulation?
Process simulation is a technique used to model, analyze, and visualize the flow of business processes in a virtual environment. It allows organizations to evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of their existing processes, identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement, and test the impact of proposed changes before implementing them in the real world. By simulating different scenarios and observing their outcomes, businesses can make data-driven decisions to optimize their operations and achieve better results.
2. Can process simulation be done in Python?
Yes, process simulation can be done in Python using various libraries and tools. Python offers a number of libraries, such as SimPy, DEAP, and SALib, which can be used to create discrete event simulations, agent-based models, and other types of process simulations. These libraries allow users to define custom models, simulate different scenarios, and analyze the results to inform decision-making and optimize business processes.
3. What is an example of process simulation?
An example of process simulation could be a manufacturing company analyzing its production line to identify inefficiencies and optimize throughput. First, the company would create a model of the production process, including all tasks, resources, and decision points. They would then run simulations with different scenarios, such as varying resource allocations or changing the sequence of tasks, to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement. Based on the simulation results, the company could make informed decisions to modify the production process and ultimately increase efficiency and productivity.
4. What is the goal of process simulation?
The goal of process simulation is to help businesses evaluate the performance of their current processes, identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks, and test the impact of proposed changes before implementing them in the real world. By simulating various scenarios and analyzing their outcomes, businesses can make data-driven decisions to optimize their processes, reduce costs, minimize risks, and improve overall efficiency. Process simulation allows organizations to experiment with different scenarios in a controlled environment and implement changes with greater confidence and understanding of their potential impacts.