Every successful business relies on countless documented processes and workflows. Yet, even the most well-organized organizations have a challenge of shadow processes. In this article, we will explore what shadow processes are and how they can be effectively avoided.
What are shadow processes?
Shadow processes are business tasks and workflows that are typically not formally tracked or monitored by the organization. These may include manual processes, undocumented activities, or informal practices that are not officially recognized or documented. Shadow processes can manifest within an organization’s operations or extend to interactions with customers and suppliers. They often introduce complexity to existing systems, generate inefficiencies, and pose potential security and compliance risks.
Companies have long sought to understand the landscape of digital work within their organizations. Various methods have been used for this purpose, including specialized consultants that map processes, flowchart-building software, and task mining and process mining tools. Nevertheless, many processes often remain undiscovered, representing the ‘dark side’ of business operations. By confronting and integrating these hidden and repressed aspects, organizations can enhance efficiency, improve compliance, and unlock their full potential.
How are shadow processes created?
There is always an ideal “happy path” for how processes should operate. This is typically documented and outlined, such as the onboarding of a new colleague by HR or the monthly closing process by Accounting. However, the happy path doesn’t always work as intended in real life. Deviations and workarounds can alter the process from its original design.
Shadow processes refer to hidden procedures that need to be completed but are not documented. These processes can overshadow the main workflow, introducing undocumented tasks and ad-hoc work. For instance, the Accounts Payable unit is responsible for invoice processing, yet it often engages in numerous small tasks that aren’t specified anywhere to ensure work continues flowing. Consequently, the process becomes much more complex than initially intended.
These hidden processes can vary widely. They may include minor adjustments within the main workflow or small deviations from assigned tasks that we inadvertently adopt. Shadow processes often consist of small procedures that people create over time without realizing it. Unfortunately, these can quickly accumulate into a significant amount of time spent when considering all the variations across the team.
Where do variations in the process come from?
- Insufficient data: When a process is poorly defined and allows for significant interpretation, people may undertake their own paths when completing a process, which may not always be the most efficient.
- Shifts in requirements: If a process has evolved—perhaps due to acquiring a new customer—yet the documented procedures remain unchanged, employees will need to adapt and find new methods on the fly.
- Redundant Work: Occasionally, employees may perform unnecessary tasks, such as rechecking certain aspects of the process to ensure smooth operation. This often occurs due to a lack of trust in software automation, leading them to manually redo parts of the workflow.
The Impact of Shadow Processes on Business
Shadow processes can significantly impact business operations, leading to inefficiencies, security risks, and compliance issues. These hidden processes add layers of complexity to existing systems, making it challenging for organizations to analyze and improve their workflows. When shadow processes are in play, management struggles to design effective strategies for non-routine situations, resulting in decreased productivity and accuracy.
Moreover, the presence of shadow processes often points to deeper issues within an organization, such as employee politics, personal preferences, and relationships. These factors can contribute to the creation and perpetuation of shadow processes, ultimately affecting the overall performance of the business.
To mitigate the impact of shadow processes, organizations can leverage high-productivity BPM cloud platforms. These platforms encourage shadow process owners to bring their processes into the light, making them more visible and manageable. By moving processes into an automation platform, businesses can reduce the prevalence of background processes and work towards achieving their efficiency and accuracy goals.
The Role of the Shadow Self in Business Processes
Carl Jung’s concept of the shadow self refers to the repressed or hidden aspects of an individual’s personality. In the context of business processes, the shadow self can significantly influence how tasks are performed and decisions are made.
The shadow self can manifest in various ways within business processes:
- Fear and avoidance: The shadow self can cause individuals to shy away from certain tasks or decisions, leading to inefficiencies and delays.
- Procrastination: It can lead to procrastination, causing important tasks and decisions to be postponed, ultimately affecting the business’s overall performance.
- Lack of self-acceptance: The shadow self can prevent individuals from acknowledging their strengths and weaknesses, resulting in poor decision-making and ineffective task management.
To counteract the negative impact of the shadow self on business processes, individuals can engage in shadow work. This involves exploring and integrating the repressed or hidden aspects of their personality. Techniques such as seeking therapy, practicing self-reflection, and developing self-acceptance are crucial in this process.
By acknowledging and addressing the shadow self, individuals can become more aware of their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. This heightened awareness leads to improved decision-making and task management, positively impacting business processes with increased productivity, efficiency, and accuracy.
In the outer world, the shadow self can manifest through:
- Shadow tasks: Tasks performed outside formal business processes, often in secret or without proper authorization.
- Shadow systems: Systems or processes operating outside formal business processes, typically without proper documentation or oversight.
Recognizing and addressing the shadow self helps reduce the presence of shadow tasks and systems, leading to improved transparency, accountability, and efficiency in business processes.
Why are shadow processes dangerous?
As one might expect, shadow processes consume a significant amount of time. While they may appear essential to our work, this perception often stems from their long-standing presence in our routines. Upon reevaluation, many of these processes reveal themselves to be redundant.
Shadow processes can obstruct other initiatives, such as digital transformation. They often go unnoticed because they are not easily identifiable and exist outside of enterprise systems and applications. These processes accumulate rapidly, increasing their risk to overall productivity.
It’s easy to overlook these tasks, as they do not constitute the core of our work yet often represent a substantial time investment. However, it is precisely these hidden processes that siphon away valuable time, disrupt workflow, and remain neglected.
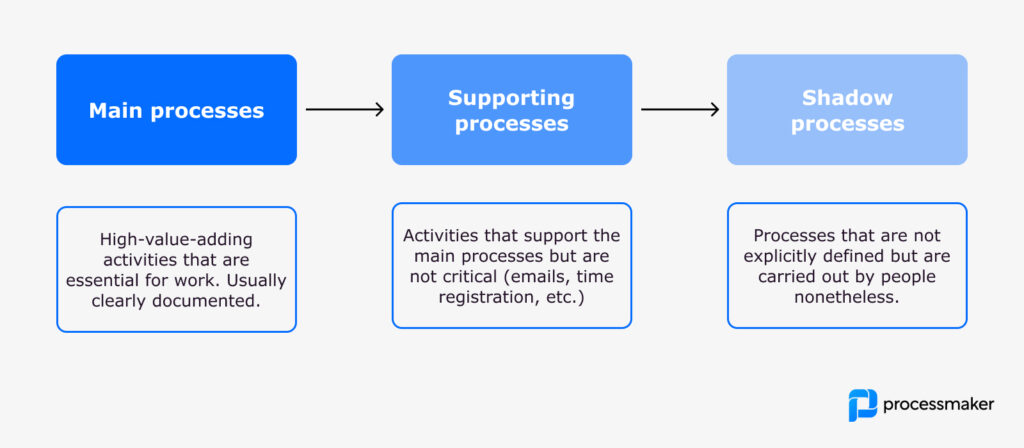
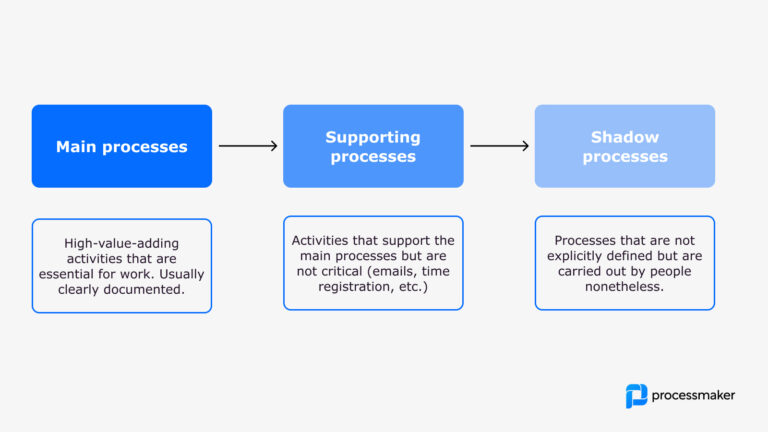
Types of processes in the organization
How can shadow processes be removed from business processes?
Shadow processes often arise when individuals attempt to eliminate tedious and ineffective tasks. Here are several strategies to eradicate shadow processes from your organization:
- Identify and document expected processes: Take the time to thoroughly document each process, along with its associated steps. Include both manual tasks and informal practices that may be contributing to inefficiencies.
- Automate processes whenever possible: Seek opportunities to replace manual processes with automated solutions. For instance, utilize software to streamline customer interactions or automate supplier management.
- Establish formal processes: Ensure that all processes are formally documented, communicated to stakeholders, and consistently tracked and monitored.
- Monitor and review processes regularly: Conduct regular reviews of your processes to verify that they remain current and that any modifications are properly documented.
- Invest in training and education: Ensure that all employees are informed about the processes and trained in their application. This investment can significantly reduce the reliance on manual workarounds.
- Seek therapy for professional guidance: Consider the option to seek therapy as an alternative to addressing shadow processes independently. A trained professional can provide guidance, spot patterns, and offer personalized prompts, enhancing the overall process.
How to discover shadow processes?
- Engage key stakeholders. Begin by interviewing stakeholders within the organization to gain insight into their processes and the manual steps they employ.
- Analyze process data. Examine data for patterns that may suggest the existence of processes that are not officially tracked or monitored.
- Observe processes in action. Spend time watching processes unfold to identify any manual steps or informal practices that might be overlooked.
- Ask pertinent questions. Pose questions that can reveal hidden processes, such as “How did you accomplish that?” or “Where did you source that information?”
- Conduct a process discovery audit. A thorough process audit can help identify shadow processes, highlight areas for improvement, and offer strategies for streamlining operations.
A new method to discover shadow processes
If you’re seeking a more automated approach to identifying shadow processes, consider using process intelligence software. Shadow processes consume significant organizational time without delivering much added value. Process intelligence software enables you to analyze internal processes, workflows, and activities, helping you uncover inefficiencies, including shadow processes. Connect with our skilled consultants to find out if this solution is right for your organization.