Was ist Hyperautomation? Anwendungsfälle & Vorteile
Wahrscheinlich haben Sie die Begriffe "Hyperautomatisierung" und "Hyperproduktivität" schon häufiger auf dem Markt für Workflow-Automatisierung gehört, aber was bedeuten diese Begriffe?
Gartner hat den Begriff "Hyperautomation" im Oktober 2019 geprägt und ihn auf den ersten Platz seiner Liste der wichtigstenTechnologietrends für 2020 gesetzt. Allerdings umfassen auch andere Branchenbegriffe das Konzept der Hyperautomatisierung. Forrester spricht zum Beispiel von "digitaler Prozessautomatisierung", während IDC und andere "intelligente Prozessautomatisierung" verwenden. Pascal Bornet, der Autor von Intelligent Automation, stellt die Verbindung zwischen intelligenter Automation und Hyperautomation her: "IA, auch Hyperautomation genannt, ist ein Konzept, das eine neue Generation der softwarebasierten Automation nutzt. Es kombiniert Methoden und Technologien zur automatischen Ausführung von Geschäftsprozessen im Auftrag von Wissensarbeitern. Diese Automatisierung wird erreicht, indem die Fähigkeiten nachgeahmt werden, die Wissensarbeiter bei der Ausführung ihrer Arbeitstätigkeiten verwenden."
Hyperautomation, ein leistungsstarkes Bündel digitaler Technologien, wird Organisationen in fast jeder Branche verändern, unabhängig vom verwendeten Begriff. In diesem Artikel erörtern wir die Hyperautomatisierung, ihre digitalen Technologien und die Vorteile, die sie bietet.
Was ist Hyperautomation?
Hyperautomatisierung ist die Verwendung von KI, ML und RPA zur Automatisierung von Aufgaben, die zuvor von Menschen erledigt wurden. Hyperautomatisierung umfasst die Automatisierung von Aufgaben und Prozessen und das Erreichen eines hohen Automatisierungsgrads. Viele Menschen bezeichnen dies als die nächste große Phase der digitalen Transformation.
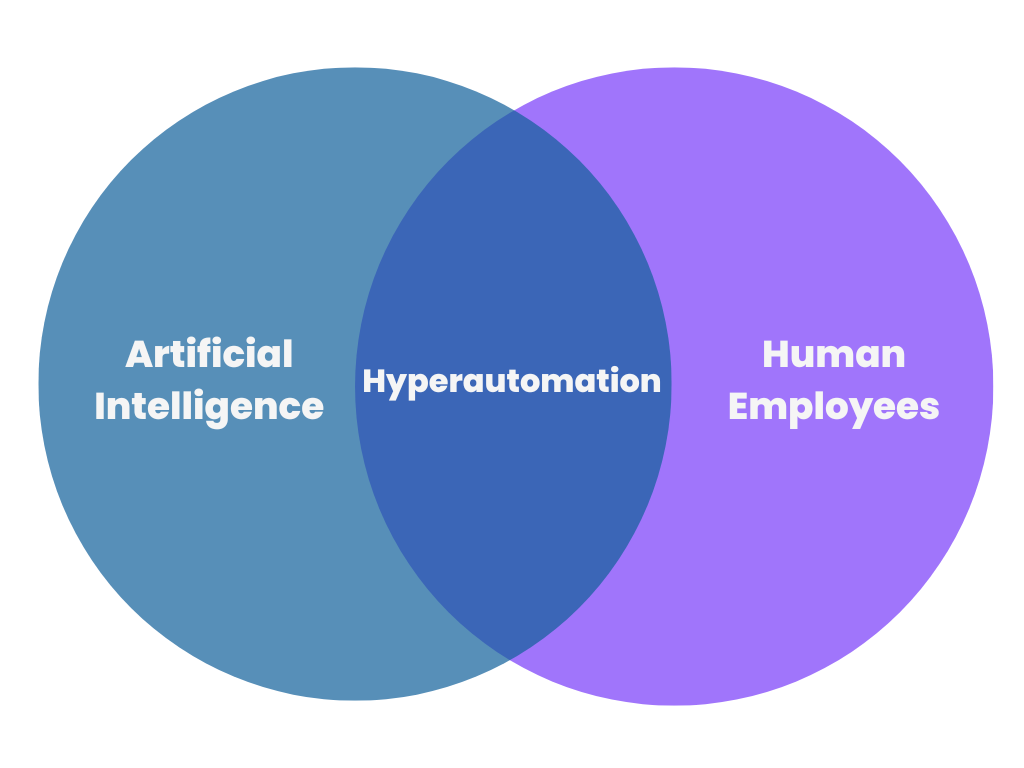
Es ist zu beachten, dass die Hyperautomatisierung nicht darauf abzielt, den Menschen vollständig zu ersetzen. Die Automatisierung entlastet den Menschen von sich wiederholenden Aufgaben und ermöglicht es ihm, sich auf höherwertige Aufgaben zu konzentrieren, die für das Unternehmen wichtig sind. Automatisierung und menschliches Engagement tragen gemeinsam dazu bei, dass Unternehmen ein hervorragendes Kundenerlebnis bieten und gleichzeitig die Betriebskosten senken und die Rentabilität steigern können.
Durch den Einsatz einer Kombination von Automatisierungstechnologien kann die Hyperautomatisierung einige der Einschränkungen überwinden, die bei der Verwendung eines einzelnen Automatisierungstools bestehen. Auf diese Weise können Unternehmen über die Grenzen einzelner Prozesse hinausgehen und nahezu jede mühsame und skalierbare Aufgabe automatisieren.
Die wichtigsten Erkenntnisse:
- Die Automatisierung erfordert eine sorgfältige Planung und Umsetzung.
- Die Unternehmen müssen verstehen, wie sich digitale Technologien in ihre neuen und bestehenden Arbeitsabläufe einfügen.
- Die Einführung der Automatisierung kann schwerwiegende Folgen haben, wenn die Rolle, die sie spielen wird, nicht berücksichtigt wird.
Die wichtigsten Komponenten der Hyperautomatisierungssoftware
Es gibt mehrere Automatisierungstechnologien, die die Hyperautomatisierung umfassen. Dazu gehören:
- Robotergestützte Prozessautomatisierung (RPA)
- Geschäftsprozessmanagement (BPM)
- Künstliche Intelligenz (KI) und/oder maschinelles Lernen (ML)
- Erweiterte Analytik
Robotergestützte Prozessautomatisierung (RPA)
Die erste Welle der Automatisierungstechnologien stützte sich weitgehend auf die robotergestützte Prozessautomatisierung (RPA). RPA beinhaltet den Einsatz von Bots zur Nachahmung sich wiederholender menschlicher Aufgaben. Diese Prozesse sind regelbasiert und nutzen strukturierte Daten zur Ausführung von Aktionen.
Im Gegensatz zur künstlichen Intelligenz, die versucht, den menschlichen Intellekt zu simulieren, konzentriert sich RPA ausschließlich auf menschliche Handlungen. Bei der Hyperautomatisierung arbeiten digitale Mitarbeiter an der Seite von Menschen, um eine unübertroffene Effizienz zu erzielen.
RPA nutzt Technologien wie Software-Bots, um sich wiederholende menschliche Aufgaben zu replizieren. RPA funktioniert in der Regel für Aufgaben, die regelbasiert sind, definierte Eingaben und Ausgaben haben, wiederholbar sind und häufig vorkommen.
Eine Einschränkung von RPA ist der Bedarf an strukturierten Daten zur Erfüllung von Aufgaben. RPA ist nicht in der Lage, den Kontext zu verstehen oder zu lernen. Sie kann nicht auf unstrukturierte Datenquellen wie Bilder zugreifen und diese sinnvoll nutzen.
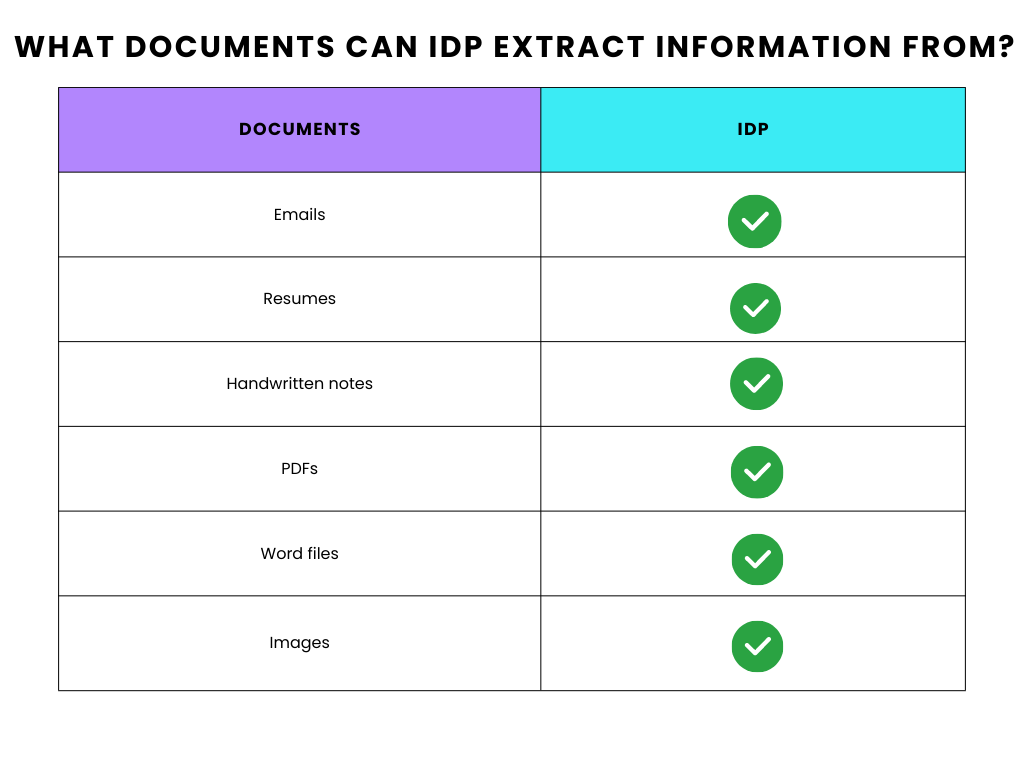
Intelligente Dokumentenverarbeitung (IDP)
Intelligente Dokumentenverarbeitung (IDP) hingegen befähigt Unternehmen, komplexere Aufgaben zu übernehmen. Im Gegensatz zu RPA eignet sich IDP hervorragend für die Organisation unstrukturierter Dokumente wie Belege, Notizen, PDFs, Word-Dateien und Bilder. Aufgrund ihrer erweiterten Funktionen ist IDP eine flexiblere Option für Ihr Unternehmen.
Software für die Verwaltung von Geschäftsprozessen (BPMs)
Die Automatisierung von Geschäftsprozessen (BPM) ist eine der wichtigsten Komponenten der Hyperautomatisierung. In vielerlei Hinsicht ist sie die Grundlage, auf der jede erfolgreiche Automatisierungsstrategie aufgebaut, überwacht und verbessert wird. Die Einführung verschiedener digitaler Tools in die Geschäftsprozesse kann eine Herausforderung sein, insbesondere für Unternehmen, die neu in der Automatisierung sind.
Unternehmen müssen neue Arbeitsabläufe erstellen und sie vor der Bereitstellung testen, um Pannen zu vermeiden. Diese Schluckaufs können katastrophale Folgen für ihr Unternehmen haben.
Künstliche Intelligenz und/oder maschinelles Lernen
Künstliche Intelligenz (KI) ist eine Methode, bei der Computer so arbeiten, dass sie die menschliche Intelligenz simulieren. Unternehmen nutzen KI, um bestimmte Aufgaben auszuführen, ohne ausdrücklich dafür programmiert zu sein. KI umfasst virtuelle Assistenten wie Siri und Alexa sowie Marketingtechnologien, die auf der Grundlage früheren Verhaltens Produkte vorschlagen. Im Jahr 2023 nutzen etwa 36 % der Menschen Apples Siri und 25 % Amazon Alexa.
Maschinelles Lernen (ML) ist ein Zweig der künstlichen Intelligenz, der Computeralgorithmen einsetzt, um Systeme im Laufe der Zeit automatisch zu verbessern. Unternehmen verwenden sowohl überwachte als auch nicht überwachte Algorithmen, um Muster in Daten zu erkennen. Überwachte Algorithmen erstellen Eingaben und Ausgaben, bevor sie selbständig Vorhersagen treffen. Unüberwachte Algorithmen beobachten strukturierte Daten und entwickeln Erkenntnisse aus der Mustererkennung.
KI erhöht die Effizienz, verbessert die Produktivität und macht zeitraubende Aufgaben überflüssig.
KI und ML sind leistungsstarke Automatisierungswerkzeuge. Ihre Implementierung kann jedoch eine erhebliche Investition von Ressourcen und eine sorgfältige Planung erfordern, um die Integration mit anderen Technologien und Prozessen zu gewährleisten. Aus diesen Gründen erfordert das Erreichen der Hyperautomatisierung den strategischen Einsatz von KI und ML.
Text zur Verarbeitung
Eine Möglichkeit für Unternehmen, KI für die Hyperautomatisierung zu nutzen, sind Text-to-Process-Funktionen oder KI-Prozessgeneratoren, -Modellierer usw. Bei ProcessMaker haben wir im Sommer 2023 unsere Text-to-Process-Funktion vorgestellt. Diese bahnbrechende Funktion ermöglicht es den Nutzern, innerhalb von Sekunden Prozesse zu entwerfen, ohne dass sie technische Erfahrung benötigen. Die Verarbeitung natürlicher Sprache (NLP) entwirft und vereinfacht diese komplexen Prozesse und verbessert so die Kundenerfahrung, die Benutzererfahrung und die Customer Journey.
Diese Art von Technologie rationalisiert Projekte in nie dagewesener Geschwindigkeit und verwandelt einfache Produktivität in Hyper-Produktivität.
Erweiterte Analytik
Hyperautomation bietet Unternehmen leistungsstarke Analysewerkzeuge und -funktionen und überwindet damit die Datenbeschränkungen, die durch ein einzelnes Automatisierungswerkzeug wie RPA entstehen. Während RPA auf strukturierte Daten beschränkt ist, können Hyperautomatisierungstechnologien sowohl strukturierte als auch unstrukturierte Daten verarbeiten. Dies hilft Unternehmen, auf Daten zuzugreifen und diese zu analysieren, die traditionell unzugänglich waren, um wichtige Erkenntnisse auf Unternehmensebene zu gewinnen.
Hyperautomation kann auch unstrukturierte Daten in strukturierte Daten für die Verwendung mit RPA-Technologien umwandeln. Diese Beziehung ist ein Beispiel dafür, wie verschiedene digitale Werkzeuge nahtlos zusammenarbeiten, um unübertroffene Effizienz zu bieten.
Vorteile der Hyperautomatisierung
Hyperautomatisierung bietet viele Vorteile und potenziell unbegrenzte Möglichkeiten. Einige der wichtigsten Vorteile der Hyperautomatisierung sind:
- Flexibilität. Da die Hyperautomatisierung auf einer Vielzahl von Automatisierungstechnologien beruht, können Unternehmen die begrenzten Vorteile einer einzelnen digitalen Technologie überwinden. Dies hilft Unternehmen, Skalierbarkeit und Flexibilität im Betrieb zu erreichen.
- Verbesserte Mitarbeiterproduktivität. Durch die Automatisierung von Aufgaben können die Mitarbeiter mit weniger Ressourcen arbeiten und eine wichtigere Rolle im Unternehmen übernehmen.
- Integration. Mit Hyperautomation können Unternehmen digitale Technologien in ihre Prozesse und Altsysteme integrieren. Die Beteiligten haben besseren Zugang zu Daten und können nahtlos im gesamten Unternehmen kommunizieren.
- Verbesserter ROI. Hyperautomation steigert den Umsatz und senkt die Kosten. Mit leistungsstarken Analysetools und -funktionen können Unternehmen den Einsatz ihrer Ressourcen optimieren.
Insgesamt vereinfacht die Hyperautomatisierung Ihre Arbeit, indem sie den manuellen Aufwand reduziert, Fehler minimiert, die Konsistenz verbessert, eine bessere Aufgabenverwaltung ermöglicht und Wachstum und Veränderungen berücksichtigt. Durch den Einsatz von Hyperautomatisierung können Sie sich auf höherwertige Aktivitäten konzentrieren, die Produktivität steigern und bessere Ergebnisse bei Ihrer Arbeit erzielen. Chatten Sie mit uns, um mehr über BPA zu erfahren und welche Software für Sie geeignet ist.