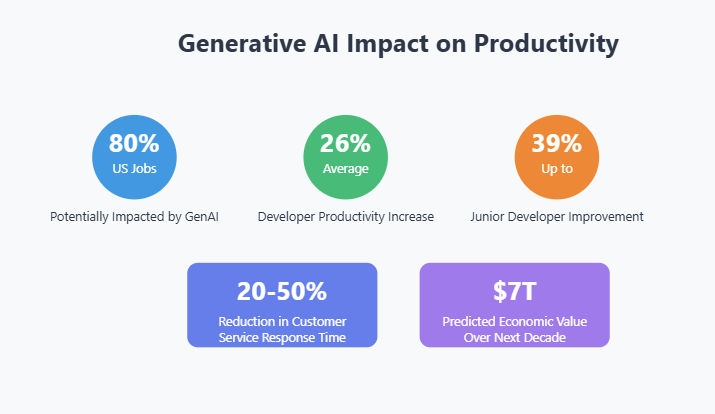
Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to revolutionize the business landscape, particularly in the realm of process automation. However, many organizations still face significant challenges when implementing AI solutions. Understanding these barriers is the first step toward successful AI adoption in business process management.
The Promise of Agentic AI in Business Processes
Agentic AI—AI systems that can act autonomously—represents a paradigm shift in business process automation. These systems can make decisions, execute tasks, and adapt to changing conditions with minimal human intervention. Yet, despite their potential, many organizations struggle to implement agentic AI effectively.
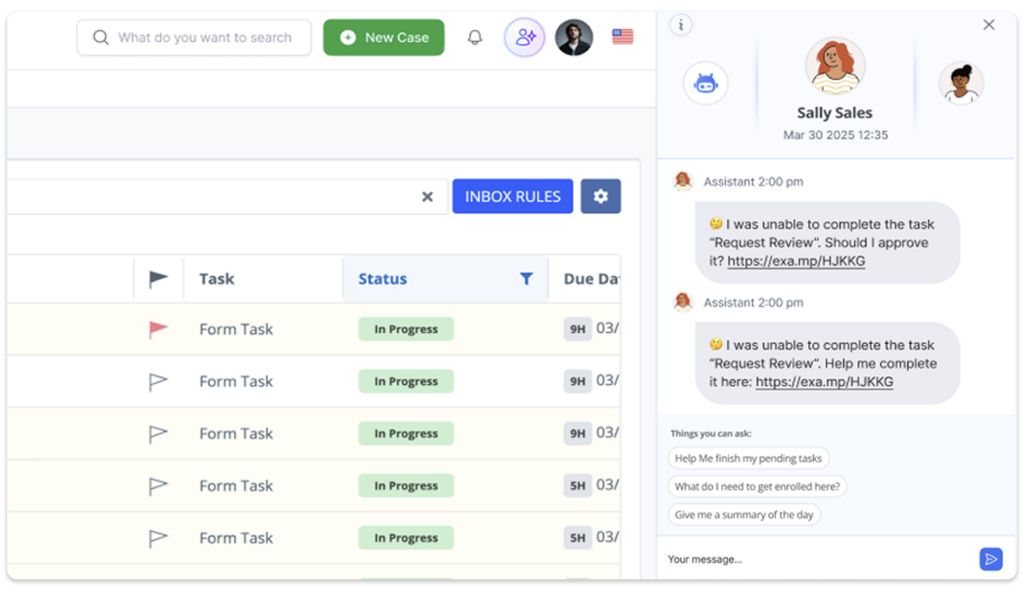
ProcessMaker’s Agentic AI automation platform
Key Barriers to AI Adoption in Automation
1. Data Quality and Accessibility Issues
For AI-powered automation to function effectively, it requires access to high-quality, well-structured data. Many organizations face challenges with:
- Siloed data across departments
- Inconsistent data formats
- Lack of historical data needed for AI training
- Privacy and security concerns limiting data access
Without a solid data foundation, even the most sophisticated AI automation tools can fail to deliver expected results.
2. Integration Complexities with Legacy Systems
Many established companies operate with legacy systems that weren’t designed with AI integration in mind. Challenges include:
- Outdated infrastructure that can’t support modern AI requirements
- Lack of standardized APIs for seamless connections
- Incompatible data storage systems
- High costs associated with modernizing infrastructure
These integration hurdles often slow down or completely derail AI adoption in business process automation.
3. Organizational Readiness
AI adoption depends not just on technical skills but also on an organization’s readiness in terms of culture and mindset. Resistance to change and a lack of trust in AI-driven systems can pose significant challenges. Even with well-designed automation plans, skepticism and hesitation among staff can hinder implementation.
For example, an HR department trying to use AI for recruitment may encounter pushback from employees who question the reliability of algorithms in assessing candidate potential.
4. Unclear ROI and Value Proposition
Decision-makers often face challenges when trying to quantify the benefits of Agentic AI in automation. Measuring intangible benefits, such as improved decision-making, can be difficult, and calculating long-term value against upfront implementation costs adds another layer of complexity.
Additionally, there is uncertainty about how AI will impact existing KPIs, and a lack of industry benchmarks in process automation further complicates the evaluation process. Without clear ROI metrics, securing budget approval for AI initiatives becomes significantly more challenging.
5. Governance and Ethical Considerations
As AI takes on more autonomous decision-making in business processes, governance becomes increasingly important:
- Concerns about algorithmic bias in automated decisions
- Lack of clear accountability frameworks for AI-driven processes
- Regulatory compliance uncertainties in different jurisdictions
- Need for transparent AI systems that can explain their decisions
Organizations must address these governance issues to build trust in their AI-powered automation systems.
Overcoming Barriers to AI Adoption in Process Automation
1. Start with Well-Defined Use Cases
Rather than attempting to transform all processes simultaneously, identify specific high-value use cases where AI can deliver immediate benefits. This targeted approach allows organizations to demonstrate concrete value and build internal expertise quickly, while addressing integration challenges.
If we use HR departments as an example, there are several specific workflows that have benefited from AI-powered automation. These include:
- Employee onboarding
- Employee offboarding
- Leave of absence
- Training request
- Remote work requests
Here, you can explore these and other success stories from organizations that have successfully selected and prioritized the right automation use cases to achieve the highest ROI for their specific business challenges.
2. Invest in Easy-to-Use AI Automation Platforms
No-code and low-code platforms democratize access to AI capabilities by allowing non-technical staff to create and modify automated processes.
For example, ProcessMaker’s drag-and-drop design studios let you design and build even the most complex workflows in no time.
AI features like text-to-process, image-to-process, process documentation, and process translation significantly accelerate the automation process. This lowers the bar for automation, allowing more organizations and a wider variety of users to have access to such technologies.
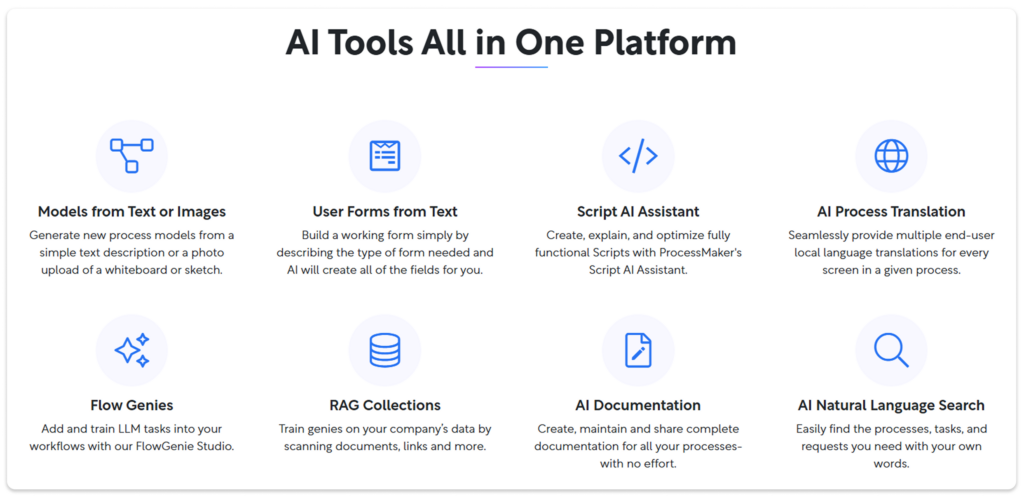
AI tools within ProcessMaker’s AI-powered business process automation platform
3. Prioritize Change Management
Technical implementation is only half the battle—organizational adaptation is equally important:
- Involve employees in the automation journey from the start
- Provide comprehensive training on new AI-powered systems
- Emphasize how AI augments rather than replaces human capabilities
- Create clear career paths for employees to develop AI-related skills
4. Establish Clear Metrics and Governance
Set up frameworks to measure, monitor, and manage AI in business processes:
- Define specific KPIs for each AI implementation
- Create governance structures for AI oversight
- Establish ethical guidelines for AI use in automation
- Implement monitoring systems to track AI performance and compliance
The Future of AI in Business Process Automation
As organizations overcome these barriers, we can expect AI to transform business process automation in several ways:
- Predictive process optimization: AI will increasingly anticipate process bottlenecks and recommend optimizations before problems occur.
BPA platforms like ProcessMaker already provide their users with continuous insights through their process intelligence tools.
- Autonomous process execution: Agentic AI will handle complete end-to-end processes with minimal human oversight, particularly for routine operations.
- Adaptive workflows: AI-powered processes will automatically adjust to changing business conditions, customer needs, and market requirements.
Conclusion
While barriers to AI adoption in business process automation exist, they are not insurmountable. Organizations that take a strategic, incremental approach to implementation—focusing on data quality, integration capabilities, skills development, and clear metrics—can successfully leverage AI to transform their operations and accelerate automation.
The most successful implementations will balance technological capability with organizational readiness, ensuring that AI-powered automation delivers sustainable value. As Agentic AI continues to evolve, organizations that overcome these adoption barriers will gain significant competitive advantages through more efficient, adaptive, and intelligent business processes.