In today’s fast-paced digital era, automation is not just a buzzword but a pivotal strategy that empowers organizations to achieve operational excellence and drive growth. Many enterprise leaders are exploring ways to harness automation for a competitive edge, while others are contemplating its impact on the workforce.
In this guide we dig deep into the topic of intelligent automation, going through key topics, examples, and best practices to help executives understand and make use of the opportunity.
What is intelligent automation?
Intelligent automation is the use of technology such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotic process automation (RPA), and machine learning to automate mundane, repetitive tasks. Intelligent automation helps to streamline processes, cut costs, and improve the efficiency of business operations.
Techs like ChatGPT and Midjourney have transformed our lives completely in such a short time. But automation isn’t an unproven tech stretching its legs for the first time. For example, RPA bots date back to the 2000s, where businesses used it to crunch numbers and populate Excel spreadsheets with content. Today, artificial intelligence is launching a new era of automation: intelligent automation.
While the interpretations of intelligent automation differ greatly between experts and organizations, you can consider IA to be powered by different technologies like:
- Artificial intelligence
- Machine learning
- Computer vision
- Robotic process automation
- Intelligent document processing (IDP) and natural language processing (NLP)
The combination of these technologies creates a sophisticated system that can handle complex tasks—without human intervention.
Roots in business process management
To a large degree intelligent automation emerged from the field of business process management – a structured and efficiency-focused way to manage business operations. The term IA itself was coined in 2017 by the analyst firm Forrester as part of their research into enterprise automation frameworks.
You can consider IA to be an advanced form of intelligent process automation – where the core goal is to develop processes and workflows that improve the way work is done with advanced technology and software.
Intelligent automation vs. hyperautomation
Intelligent automation is sometimes referred to as hyperautomation – a term coined by Gartner. In Gartner’s definition, hyperautomation is “a business-driven, disciplined approach that organizations use to rapidly identify, vet, and automate as many business and IT processes as possible.”
According to Gartner, hyperautomation involves the orchestrated use of multiple technologies, tools, or platforms, including: artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, event-driven software architecture, robotic process automation (RPA), business process management (BPM) and intelligent business process management suites (iBPMS), integration platform as a service (iPaaS), low-code/no-code tools, packaged software, and other types of decision, process, and task automation tools.”
At first glance, hyperautomation and intelligent automation appear similar. While they’re often used interchangeably, they differ in one key area.
Hyperautomation is a mindset. It expands the range of technologies beyond the process-specific; like digital twins, IoT sensors, and even robotic arms. Intelligent automation is one of the possibilities to satisfy the mission of hyperautomation.
Is intelligent automation part of digitalization?
Intelligent automation is a major driver of digital transformation as it highly impacts all three components of digital work: people, processes, and technology.
At a deeper level, intelligent automation empowers the six key success factors that drive digital transformation forward:
- Strategy – achieving a competitive advantage by leveraging a digital-first strategy;
- Organization – enabling the future of work by augmenting the modern workforce;
- Culture – democratizing data and insights, enabling value across all levels of the enterprise organization;
- Technology – connecting the best of human and artificial intelligence where technology augments experience;
- People – giving people more meaningful work without copy-paste talent waste;
- Customer experience – streamlining and improving the fully digitalized customer experience.
Intelligent automation & AI
Another common source of confusion is between IA and AI. Artificial intelligence algorithms and platforms can be used within intelligent automation, but AI is also adapted across many other use cases outside of business process management. Generally, the two terms should not used interchangeably.
Many intelligent automation solutions have embedded artificial intelligence in the form of machine learning (ML) algorithms. You can think of machine learning as either supervised or un-supervised work where machines adapt and learn for themselves to make improvements based on available data.
You may not always see machine learning in action, but it’s helpful to ask vendors where it is being used. Just like with intelligent automation overall, ML is typically applied in mundane, routine tasks that humans don’t want to do.
Is intelligent automation replacing employees?
Will intelligent automation replace the human workforce? In a short answer: no.
We can’t fully predict the future of work but one thing is clear. While automation won’t replace all jobs, it will impact 100% of jobs within the next decade.
Generally, IA is seen as an opportunity to augment human intelligence in the workforce, where it can efficiently take on mundane, repetitive tasks, freeing up workers to take on more creative elements of their work.
Another way to see it is that intelligent automation doesn’t replace the human, it takes the robot out of the human.
On the other hand, there are many job roles that are directly impacted by automation. In the Future of Jobs Report, the World Economic Forum estimates that artificial intelligence alone will replace 85 million jobs worldwide by 2025. In the table, they have identified examples of jobs that have already been replaced by automation in the United States.
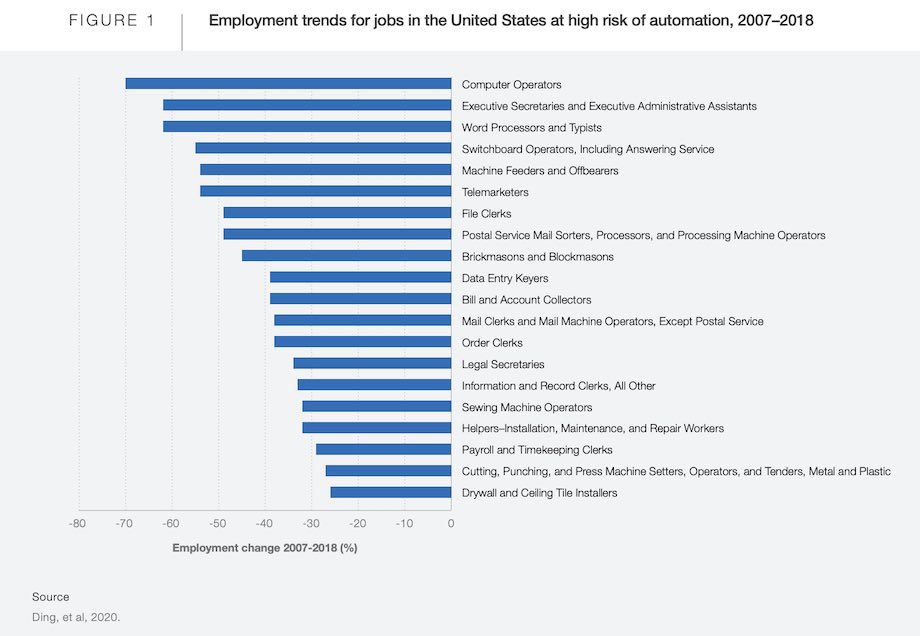
Examples of jobs at risk from automation 2007-2018 study. Source: World Economic Forum
Benefits of intelligent automation for business
It’s no surprise that 35% of companies are already using intelligent automation in their business. Amongst the latecomers, 35% are busy exploring the right AI tools for their teams. What are the chief advantages of intelligent automation for today’s businesses?
Cost savings
By blending automation with AI, McKinsey reports companies can unlock up to 20% in labor savings. The analysts at Accenture predict AI can drive a 38% increase in overall profitability. With each day, artificial intelligence tools become even more accessible, shattering cost-saving estimates in the process.
Accuracy
Human errors love to slip into spreadsheets. One errant keystroke can rack up fines into the millions—like TransAlta’s cut-and-paste mishap that cost the power company $24 million. For tasks that require a strict recipe of clicks and keystrokes, software bots can handle the job with higher accuracy than humans.
Customer satisfaction
The right combination of IA tools can build a base of happy, loyal customers. Manual processes that are too slow are a customer drain: 49% of consumers report ditching a company after one bad experience. And that’s just over a one-year period.
On the other hand, always-ready chatbots, faster processing, and rapid approval timelines can change a satisfaction score from slumped to soaring.
For example, applying for a small business loan used to be a frustrating affair involving hours of appointments, paperwork, and wet signatures. Now, IA can run fraud checks, compile applicant data, and automatically pit applications against internal business rules. Providers can deliver instant decisions right from a self-service portal.
Efficiency and Productivity
IA means more than a boost to the hard numbers: the savings tip soft numbers, too. One study by the University of California reveals that motivated employees are 31% more productive. They also close a whopping 37% more sales rather than discourage their counterparts. Simply put: exciting work thrills top talent. By cutting back on the mundane, you can improve your team’s output.
These are just a handful of the benefits one-third of companies using IA are currently enjoying. Let’s explore how top businesses use intelligent automation.
Why automate business processes?
Processes are the lifeblood of business operations. Each organization is built up of thousands or millions of tasks, workflows, and processes where different teams and resources interact to create products or services and bring value to customers.
As business operations have advanced and matured, process excellence has become a source of competitive advantage. Many organizations have turned to digital process management and technology to keep ahead of the competition.
Digitalization has not only been a blessing, but it has come with many challenges to the workforce. Employees working with repetitive tasks across different digital systems struggle with swivel chair processes, while the large number of new apps and new tools used has led to an increase in shadow processes. Ultimately, digitalization is a new resource that needs to be systematically documented, analyzed, and utilized – and that’s where automation comes in.
How does intelligent automation work with business process automation?
Intelligent automation can be seen as the adoption of an assembly line concept to business processes, breaking tasks into repetitive steps and digital processes. Instead of having skilled employees manage each step, intelligent automation involves creating a digitally enabled workforce where some tasks are done through automation technology.
Here are some examples of how all departments can use IA technologies in their business processes.
Artificial Intelligence
- Marketing: BuzzFeed swept social media attention with quizzes musing over which Twilight character wanted to marry you. Now, they use AI to craft on-the-spot short stories gazing into your future like the middle-school game MASH.
- Operations: A predictive maintenance process picks up an IoT sensor: a delivery truck’s tire pressure is running low. IA can schedule an available technician to have a look when the vehicle returns to HQ.
- Customer Service: Chatbots and virtual agents can hold lifelike conversations with customers. Retailers can provide delivery updates, or e-commerce brands can use them to dispense product advice on chat apps.
Machine Learning
- Sales: An RPA bot imports information from a signed agreement into your accounting system.
- Marketing: Some online shopping sites, such as flight booking or drop-shipping, use machine learning to price dynamically. Algorithms analyze competitor pricing, demand, and historical sales to adjust prices in real time.
- Accounting: Machine learning algorithms can analyze transactional data and identify unusual patterns that might indicate fraudulent activities like money laundering, embezzlement, or unauthorized transactions.
Natural Language Processing
- Marketing: NLP can scour thousands of product reviews to rate customer sentiments. Determine whether your users are having a positive or negative experience and tweak accordingly.
- Human Resources: HR executives use NLP to help computers read incoming data from resumes and applications. They can then use the insights to shortlist rockstar candidates.
- Manufacturing: Use NLP to analyze materials like maintenance and service reports to identify patterns and trends related to equipment failures or breakdowns. NLP can yank key information like issue descriptions or timestamps (even from handwritten text!) to identify common maintenance problems and predict potential failures.
Intelligent Document Processing
- Records: Medical offices use intelligent document processing to process patient charts, lab reports, and physician notes. IDP can turn handwritten notes into digital documents, and then extract relevant information like medications, diagnoses, and treatment plans.
- Legal: IDP is a boon for patent analysis, a process that’s rich in technical information. IDP systems enlist NLP and machine-learning algorithms to scour claims, descriptions, and citation data to identify potential infringements.
- Onboarding: Banks use OCR and ML to extract relevant data from new account openings or loan requests. Extract relevant data from passports, driver’s licenses, or utility bills to run through automated KYC processes. IDP bolsters regulatory protections by categorizing and filing incoming paperwork, too.
These are just some of the ways you can supercharge your business processes with the near-magic of artificial intelligence.
6 more examples of intelligent automation
- Healthcare: Using AI-powered chatbots to respond to patient queries and robotic process automation (RPA) to automate administrative tasks.
- Retail: Using automated inventory systems for better inventory management and customer experience.
- Banking and finance: Using AI-powered fraud detection and automated loan approval workflows.
- Manufacturing: Using robots to automate production lines or automate order fulfillment.
- Logistics and transportation: Using AI-powered systems for route optimization.
- Insurance: Using process intelligence to streamline or automate claims processes.
A 6-step framework for intelligent automation
When you’re building out your intelligent automation strategy it’s important to recognize the time and resources required for effective implementation.
IA should be considered a journey and not a destination – requiring considerable strategic planning. You can leverage this six-step framework to get started.
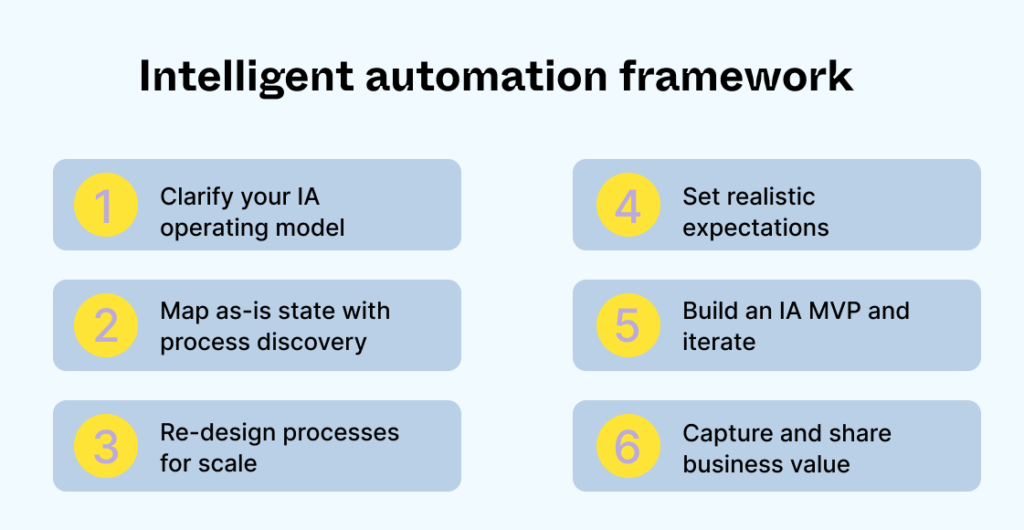
- Clarify your IA operating model. A good starting point is a clear understanding of the overall strategy. Start by describing the goal and steps needed to achieve it.
- Leverage process discovery. For many organizations, the first starting point for automation is process discovery – where you identify the biggest areas for improvement.
- Design for wide-scale implementation. Many organizations take a test-and-learn approach to IA. While it’s good to prove new concepts, identify test cases with measurable impact on key business goals.
- Set realistic expectations. Any changes to business processes will impact your workforce and culture. Invest in robust change management communications.
- Build a minimum viable product (MVP). Intelligent automation can require significant effort and resources. Consider developing an MVP to prove results before rolling out through a large implementation.
- Capture and communicate value. Automation in itself does not make business processes better. Identify and measure concrete ways that IA improves your key business metrics. Once you’ve reached the finish line it’s time to start again!
Business and IT collaboration in automation
Business leaders and IT should collaborate in the adoption of intelligent automation in order to ensure successful and compliant implementation.
IT professionals can provide the technical expertise to help set up and maintain the necessary infrastructure, while business leaders can provide the business knowledge and insights to ensure that the technologies are used in the most effective and efficient manner.
Collaboration can also help to identify the best opportunities for automation and ensure that the technologies are used to their full potential.
The importance of data culture
Most companies implementing intelligent automation face challenges with data quality, but an equally or even more important question is the level of data culture.
Data culture is the collective behaviors and beliefs of people who use data to improve decision-making. You can consider an organization data-driven when data is embedded into decision-making, operations, mindset, and the identity of an organization.
Many organizations face resistance to data culture when they disrupt existing ways of working or implement new tools, processes, or workflows. Having a strong data culture helps an organization adapt effectively to change in a way that leverages the skills and experiences of the workforce.
A good data culture improves the level of data literacy and empowers employees to ask the right questions, find insights, and improve ways of working as well as the employee experience by eradicating inefficiency and wasted work.
Intelligent automation tools and software
There are many software solutions and tools for enterprise businesses to adapt intelligent automation. Common examples include:
- Business process automation (BPA) software
- Business process management platform
- Process intelligence software
- Process mining software
- Robotic process automation tools
- Integration platforms as a service, iPaas
- Intelligent document processing
Rarely is one software used for all intelligent automation needs. In most cases, enterprise organizations develop a modern intelligence and automation stack.
Moreover, many advanced BPA tools combine several technologies in one platform. For example, ProcessMaker combines advanced business process automation, process intelligence, and intelligent document processing tools all in one end-to-end AI-powered platform.
Exploring the benefits of Intelligent Automation? Contact us to transform your workflow and business processes.





