Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is widely used by both business owners and technical users to design and implement business processes. Yet BPMN 2.0, a 500+ page ISO standardized specification, can be confusing to those unfamiliar with business process management. Keep reading for a brief overview of what BPMN 2.0 is, its origins, applications, advantages, and a detailed exploration of its elements and symbols.
What is BPMN 2.0?
BPMN 2.0 is more than just a notation system; it’s a universally recognized language for modeling business processes. BPMN 2.0 is an open standard notation system based on a flowcharting technique that’s used to model business processes. The standard is widely used in business process management since it’s easily understood by business users while also providing technical users with the ability to represent and implement complex processes, enabling the two groups to collaborate effectively.
See for yourself! Try out the latest features of ProcessMaker Platform for free.
BPMN 2.0: a brief history
To truly appreciate BPMN 2.0, it’s essential to understand its historical context. BPMN was originally developed by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI) in 2004. However, in 2005, a pivotal merger took place when BPMI joined forces with the Object Management Group (OMG). This merger played a significant role in shaping the future of BPMN.
One year later, in 2006, BPMN was formally adopted as a standard by OMG, marking a crucial milestone in its development. The move from BPMN 1.0 to BPMN 2.0 occurred in 2010, but BPMN 2.0 wasn’t officially released until 2013. The standard’s worldwide recognition came when it was published by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) under the designation ISO/IEC 19510.
BPMN 2.0 uses and benefits
The primary purpose of BPMN 2.0 is to create clear and comprehensible business process model flowcharts. Similar to other business process modeling tools, BPMN 2.0 acts as a common language that facilitates understanding among stakeholders. Whether you’re a business owner looking to streamline operations or a technical expert responsible for implementing these processes, BPMN 2.0 caters to your needs.
AI Modeler
With the ProcessMaker AI Modeler, your organization can design a process map in seconds just by using your own words. ProcessMaker’s text-to-process or process generation functionality also doesn’t require any advanced tech experience. It’s an accessible, easier, faster way of creating a process map. Check out our text-to-process free trial to see how it works.
Advantages of BPMN 2.0
Enhanced Understanding
BPMN 2.0 provides a visual representation of the steps involved in a business process, making it easy for business users to grasp how a process functions. This clarity is invaluable for decision-making and process improvement.
Implementation-Ready
At a technical level, BPMN 2.0 offers enough detail to implement a process efficiently. It provides a blueprint that technical teams can follow, ensuring consistency and reducing errors during the implementation phase.
Improved Collaboration
One of BPMN 2.0’s key strengths is its ability to bridge the gap between different stages of business process management. It facilitates collaboration between stakeholders with varying functions, enabling them to work together seamlessly.
Seamless Integration
BPMN 2.0 offers compatibility with XML-based BPMN formats, making it easy to convert business process diagrams into process models. This feature streamlines the process of implementing and executing processes.
In essence, BPMN 2.0 offers a versatile solution that benefits organizations by improving process understanding, streamlining implementation, fostering collaboration, and ensuring seamless integration.
BPMN 2.0 elements and symbols
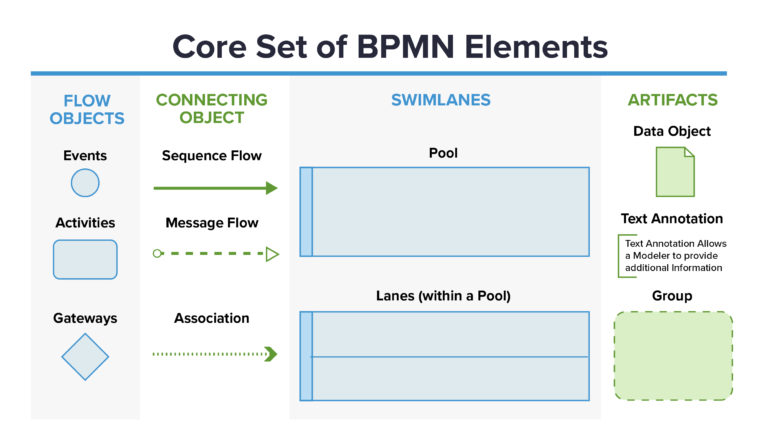
As a standard language for modeling business processes, BPMN 2.0 employs a range of symbols and elements to represent different aspects of a process. These symbols can be categorized into four main groups:
Flow objects
Flow objects are the backbone of the overall workflow. The three main flow objects are called events, activities, and gateways. Events are triggers that start, alter, or complete a process. Activities are tasks performed by individuals or technology, while gateways function as decision points in the process flow.
Swimlanes
Swimlanes are used to organize and illustrate the participation of different entities or participants in a process. Each swimlane provides a visual separation of activities associated with specific participants, making it easier to identify roles and responsibilities.
Connecting objects
Connecting objects represent how the elements of a process relate to one another. There are three types of connecting objects: sequence flows, message flows, and associations. Sequence flows define the order in which activities will be performed. Message flows depict communications between departments, while associations demonstrate the relationship between an artifact and an event, activity, or gateway.
Artifacts
Artifacts are used to provide additional information about a process. There are three types of artifacts: data objects, groups, and annotations. Data objects specify what data is required for a particular activity. Groups display the logical grouping of activities. Annotations are used to explain various aspects of the diagram, adding context and clarity.
See for yourself! Try out the latest features of ProcessMaker Platform for free.
ProcessMaker and BPMN 2.0
To harness the full potential of BPMN 2.0, it’s essential to choose the right tools and software. For example, ProcessMaker, a leading low-code business process management software, offers a solution that simplifies the design, testing, and implementation of business processes, all while adhering to BPMN 2.0 standards.
ProcessMaker’s software empowers organizations to streamline their operations by providing a user-friendly platform for designing and implementing BPMN 2.0-compliant processes. It offers the following features:
Low-Code Platform
ProcessMaker’s low-code approach enables users with varying technical backgrounds to design and implement complex processes. This accelerates the development cycle and reduces the reliance on traditional coding.
Automation and Integration
ProcessMaker offers automation capabilities and can be integrated with other systems, enabling organizations to streamline their operations further and achieve greater efficiency.
ProcessMaker’s low-code intelligent automation software simplifies the design, testing, and implementation of business processes using BPMN 2.0. With this software, organizations can efficiently design, test, and implement their processes, unlocking new levels of efficiency and innovation and ensuring their continued growth and success. Chat with one of our automation experts to learn how you can leverage BPMN 2.0-compliant software in your organization.