Robotic process automation (RPA) is an unrivaled master when it comes to mimicking concrete instructions. The technology shifts responsibility for a manual task, like filling out an Excel spreadsheet or validating information, from a human over to a software robot. RPA is such an astute rule follower, Gartner predicts that it can save almost $1 million in human error per year within the admin-heavy finance sector.
Despite its massive potential for boosting accuracy, productivity, and efficiency, RPA programs are only as strong as the planning strategy that supports them. That’s why process analysts use a technique called process mapping. This method is the interface between a business problem and an RPA solution, providing a bot with a detailed set of instructions for completing a given task. Here are five ways analysts are using process mapping to improve their RPA initiatives.
Process mapping can help all stakeholders visualize RPA initiatives
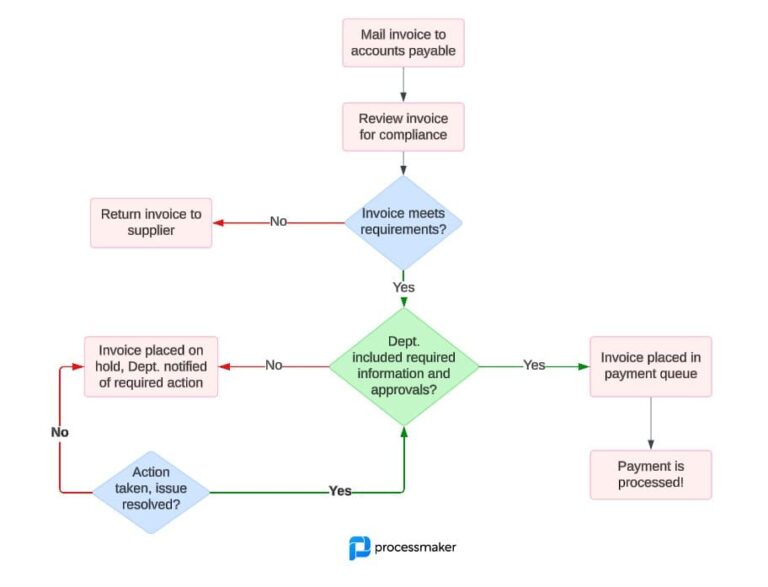
One of the most commonly used tools in process mapping is a high-level process map. It’s a quick snapshot of the steps involved in an RPA program. This handy visualization shows how different systems interact without going into extreme detail. It’s a great way to communicate how an RPA process works to leadership and non-technical stakeholders.
Using swimlanes to show how systems interact
Organizations are rife with tasks that are strong contenders for RPA. A banker checks to make sure an applicant isn’t on a watchlist. A marketing analyst compiles campaign performance information from various platforms into a spreadsheet. Customer service reps verify inventory levels, and HR reps validate timesheets and tax deductions. Using RPA, you can enlist bots to take on each of these manual tasks.
When it comes to highlighting how bots slot into the process, swimlanes are a valuable visual flowchart in a process mapper’s toolbox. Swimlanes are cross-functional maps that divide up a large project into designated “lanes” of responsibility. While you can use swimlanes to assign responsibility to individuals or departments, RPA analysts use swimlanes to illustrate what systems or technologies will handle a task.
Use a value stream map to balance automation and customer satisfaction
Don’t get locked into simply finding the most optimal sequence of tasks. Just because a process appears to be the most efficient doesn’t mean it’s delivering the most value for your end user.
Value stream mapping is one of the tools used by process mappers to make sure they always keep the customer top of mind. Does your customer service team waste hours per day resetting passwords—a job that a bot can easily perform? Maybe you’ve turned over a certain step in your sales pipeline to RPA, but a more hands-on approach is needed. Value stream mapping helps strike a balance between tactical efficiency and serving the best value to your customer.
It’s a powerful tool for identifying systemic inefficiencies
When you have a clear visual of how systems exchange information, you can more easily identify inefficiencies. Are bots frequently handing the same data back and forth between two systems? This can lead to processing delays and long customer wait times. Process maps can shed light on bottlenecks and help you find more optimized routes.
A process map can shed light on unnecessary steps
In their excitement to implement RPA technologies, many organizations simply turn over their existing manual tasks to a software system. McKinsey warns teams to be wary of this trap: the most effective RPA initiatives are the ones that start by simplifying overly complex systems.
Are you mobilizing a squadron of bots to transcribe a 25-field application? Start by considering what fields you might be able to eliminate. Still relying on an age-old monthly report template, even though management only reads a few pages out of the dozens? Instead of simply transferring these responsibilities over to RPA, a process map forces you to examine each step and identify which ones are necessary to your overall goals—and which steps are simply dead weight.
Robotic process automation is a powerful technology for increasing overall efficiency within your organization. Forrester valued the RPA market at $250 million in 2016, predicting skyrocketing growth to $2.9 billion by the end of 2021. Despite having “robot” in the name, getting the most out of this digital workforce takes just as much planning as any other initiative in your organization. Using process mapping tools, you can help your organization set a strong foundation for a successful RPA program.