Processes are the lifeblood of any organization, yet their effectiveness often remains unexamined. Understanding the magnitude of process performance is indispensable for overall business success. Let’s delve into the topic in-depth.
Importance of Measuring Process Performance
Process performance refers to the efficacy with which a business process accomplishes its intended function. It is an integral aspect of operational efficiency, linked inextricably to a company’s profitability and growth. Measuring process performance illuminates the pathway to continuous improvement, offering visibility into areas of inefficiency or underperformance. It aids in realizing organizational goals and strategies, fostering better decision-making, and driving growth.
Key Metrics for Evaluating Process Performance
Within business process analysis, process performance is often measured within a framework of process metrics or key performance indicators (KPIs.) Some of the key performance metrics include:
- Efficiency. Efficiency is the ratio of output to input in a process. High efficiency signifies optimal resource utilization.
- Effectiveness. Effectiveness measures whether the process is producing the intended results or meeting predefined objectives.
- Cycle Time. Cycle Time refers to the total time from the beginning to the end of a process. A shorter cycle time is indicative of a well-optimized process.
- Process Yield. Process Yield calculates the number of correct outputs divided by the number of total outputs. A higher yield suggests a more successful process.
Techniques to Measure Process Performance
How do we measure these metrics? The following techniques are widely utilized.
Process Mapping
Process Mapping involves creating a visual representation of the process, offering a holistic view of the entire process flow.
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
SPC employs statistical methods to monitor and control a process, facilitating data-driven decision-making.
Six Sigma Methodology
Six Sigma Methodology aims at reducing process variation and improving quality, typically leading to an increase in customer satisfaction and a reduction in cost.
Benchmarking
Benchmarking involves comparing a company’s performance with industry best practices or competitors to identify areas for improvement.
Process Mining and Task Mining
Increasingly, process performance is measured through automated process analysis tools, such as process mining software and task mining tools.
Implementing Process Performance Measurement
Let’s briefly outline the steps to implement process performance measurement in an organization.
- Define objectives: Start by establishing clear, measurable goals aligned with your organization’s strategy.
- Identify key processes: Determine the processes that significantly influence the achievement of these objectives.
- Establish metrics: Choose appropriate metrics that can effectively gauge process performance.
- Collect data: Ensure consistent data collection methods and that the data is accurate and timely.
- Analyze and act: Use the collected data to identify trends, make informed decisions, and implement process improvements.
In conclusion, understanding how to measure process performance is crucial for the operational efficiency and success of an organization. It is an ongoing process that requires the constant monitoring and reviewing of metrics, the implementation of improvements, and the adoption of a culture of continuous learning.
Keep in mind a balanced scorecard for process performance
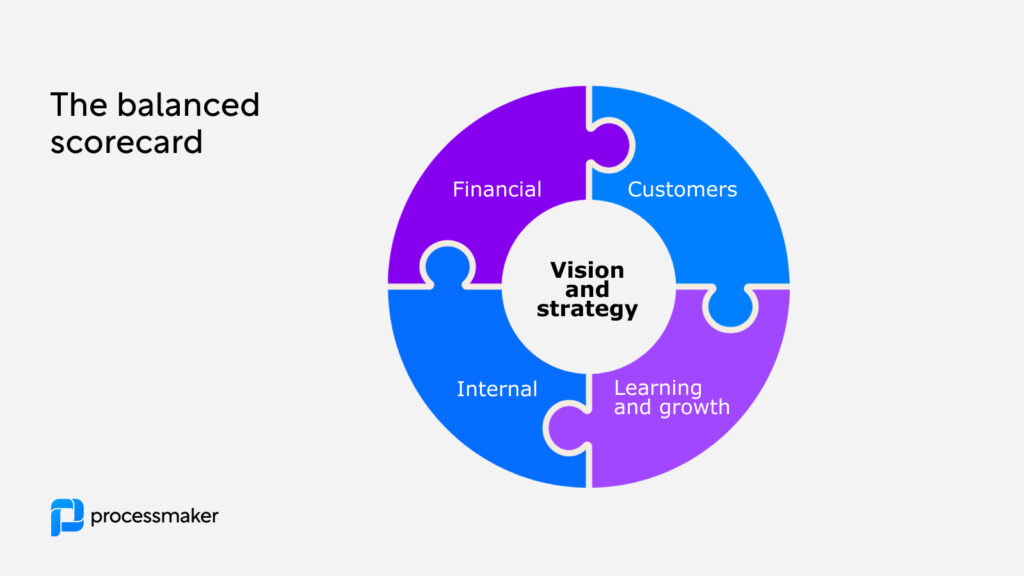
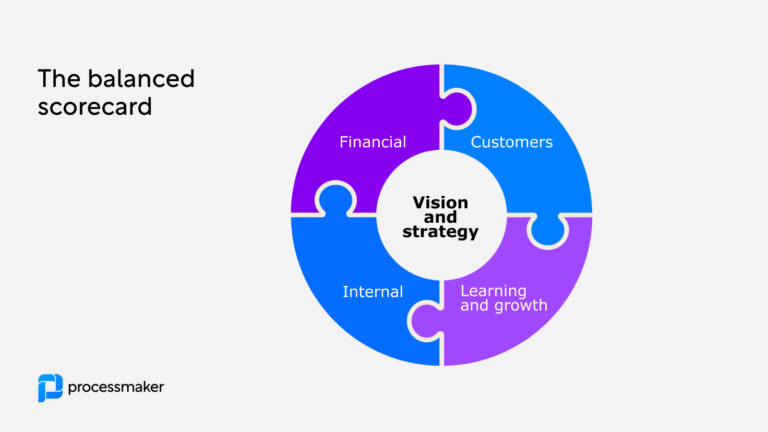
A Balanced Scorecard is a strategic planning and management system used extensively in business and industry worldwide. It translates an organization’s mission and vision into actual operational actions, spanning four main perspectives: Financial, Customer, Internal Process, and Learning and Growth. Now, how does the Balanced Scorecard tie into process performance measurement? Here’s why it’s crucial:
- Holistic View: The Balanced Scorecard offers a comprehensive view of the business by considering four critical perspectives. This holistic approach ensures that process performance is not just judged on efficiency or output but takes into account customer satisfaction, financial results, and learning and growth initiatives.
- Strategic Alignment: By linking process performance metrics with strategic objectives, the Balanced Scorecard ensures that every process aligns with the organization’s broader goals. It aids in prioritizing processes that contribute most significantly to strategic objectives.
- Cause and Effect Understanding: The Balanced Scorecard maps out the cause-and-effect relationship between different performance measures. This helps identify which processes have the largest impact on the organization’s performance and consequently need the most attention.
- Focus on Continuous Improvement: The Balanced Scorecard enables organizations to monitor progress over time and adjust strategies as necessary, fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
- Balancing Short and Long-Term Goals: By offering a balanced view of performance, the scorecard helps balance short-term operational goals with long-term strategic objectives. It helps businesses understand the trade-offs they may need to make and ensures sustainability.
Remember, performance is the foundation upon which businesses are built. Therefore, making process performance measurement a part of your organizational DNA is imperative for sustainable growth and success.