Process optimization is a core element of effective business process management. It is both an art and a science, where best practices can be implemented across different business types, but each enterprise will have unique factors to consider.
In this article we explore the different types of process optimization techniques, the steps for optimizing a process, and the challenges associated with process improvement initiatives.
What is business process optimization?
Process optimization is the systematic approach of analyzing and improving business processes to achieve maximum efficiency, effectiveness, and quality. The goal of process optimization is to continuously reduce waste, increase productivity, and ultimately improve an organization’s bottom line.
Process optimization plays a crucial role in ensuring that a company can operate efficiently, maintain high-quality standards in production or services, and meet customer expectations. By optimizing processes and reducing inefficiencies, organizations can allocate resources and focus on strategic initiatives that drive growth and profitability.
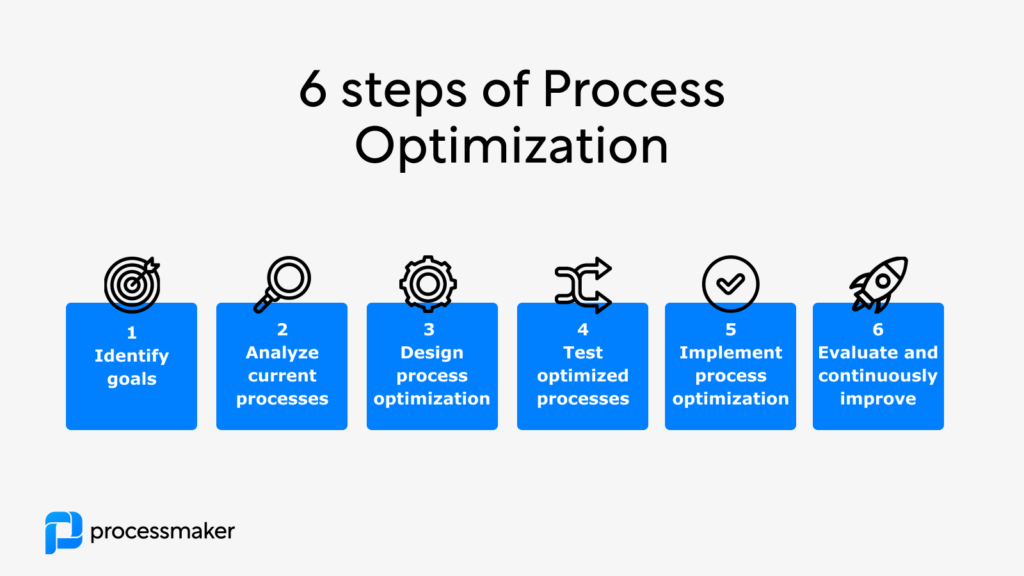
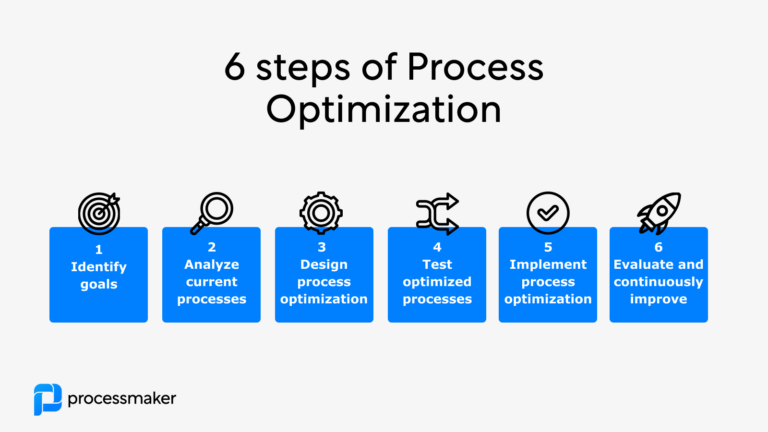
Steps for optimizing a process
Process optimization is rarely a one-off exercise. Instead, process optimization is typically a continuous process driven by operational excellence professionals who follow methodological processes to plan, analyze, and execute process improvements.
When optimizing a process in an enterprise organization, there are several steps to follow.
- Identify goals. The first step is to identify the goals of the process optimization. This will help determine the best way to optimize the process.
- Analyze current processes. Next, analyze the current processes to identify areas of improvement. This can be done through process mapping or through data analysis.
- Develop an optimized process. After identifying areas of improvement, create an optimized process based on the goals of the optimization. Make sure to include the necessary automation and technology needed to optimize the process.
- Test the optimized process. Once the optimized process is developed, test it to ensure that it meets the goals of the process optimization. This will help identify any issues or areas that need to be improved.
- Implement process optimization. Once you have your desired process improvement validated, it’s time to implement the process across your organization. In this phase, it may require additional monitoring and measuring to ensure that the optimization maintains the desired results.
- Evaluate and continuously improve. Rarely are process improvements a one-off exercise. In many organizations, you’ll expect to see a continuous analysis and refinement of core processes to achieve incremental improvement.
Types and methods of process optimization
There are several different types of process optimization techniques.
- Process mapping. Process mapping is a method used to visually document an entire process from start to finish. It helps identify areas of improvement and optimize the process.
- Process mining. Process mining is a technique used to discover, analyze, and improve business processes using data mining methods. It can accelerate and automate the data-gathering phase of process analysis.
- Root-cause analysis. Taking a step deeper into process analysis by looking not just at what has happened, but the root causes for key challenges and process challenges.
- Workflow analysis. In addition to reviewing processes or tasks, workflow analysis can be used to inspect and improve end-to-end workflows.
- Value stream mapping. Value stream mapping is the method of creating a graphic representation of the materials, data, or information valuable to a project or initiative.
In addition to process-specific techniques, there are many analytical frameworks that are relevant to process optimization.
- DMAIC. The DMAIC method is a way of data-driven optimization flowing from the acronyms (D) define, (M) measure, (A) analyze, (I) improve, and (C) control.
- Kaizen. A method of continuous improvement developed in Japan highlighting how small incremental changes can have a cumulative improvement in performance.
- PDSA. Another optimization method comprising of four stages (P) plan, (D) do, (S) study, and (A) act.
- Six Sigma. Six Sigma is a data-driven methodology for improving processes. It helps identify and reduce errors, leading to more efficient processes.
- Sipoc. A diagram technique outlining the (S) suppliers, (I) inputs, (P) processes, (O) outputs, and (C) customers of key processes.
Benefits of process optimization
There are numerous benefits to optimizing processes within an organization. Here are some of the most significant advantages:
- Cost reduction. One of the primary goals of process optimization is to eliminate waste and reduce costs. By identifying inefficiencies in existing processes and implementing changes, organizations can save both time and money. This enables them to operate more efficiently and allocate resources more effectively.
- Improved efficiency. Process optimization helps businesses identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and other obstacles that hinder productivity. By streamlining workflows and implementing best practices, organizations can improve efficiency and increase overall output.
- Enhanced quality and consistency. By standardizing processes and eliminating variations, process optimization can lead to improved quality and consistency in products and services. This, in turn, can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Increased competitive advantage. Organizations that invest in process optimization can gain a competitive advantage over their rivals. By improving efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing quality, businesses can differentiate themselves in the marketplace and attract new customers.
Top 10 Process Optimization Tools
Process optimization tools are designed to help organizations improve their business processes, identify inefficiencies, and implement automation solutions. Here are some of the top process optimization tools:
- ProcessMaker: ProcessMaker is a Business Process Automation platform that lets you optimize processes by automating complex cross-functional workflows. This is also complemented by ProcessMaker PI – a process intelligence tool – that helps companies have complete 360 visibility over all of their processes in real-time. The entire suite has a no-code approach, allowing teams to effortlessly streamline operations, improving overall productivity.
- Blue Prism: Blue Prism is a well-known RPA software that empowers businesses to automate manual, rule-based tasks across various departments, leading to increased efficiency and cost savings.
- Celonis: Celonis is a leading process mining software that enables organizations to analyze and visualize their processes. It helps identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement, facilitating data-driven decision-making.
- Kissflow: Kissflow is a cloud-based BPM and workflow automation platform that allows organizations to streamline their processes through customizable workflows, forms, and reports. Kissflow’s intuitive drag-and-drop interface makes it easy for users to create and modify processes, even without technical expertise.
- UiPath: UiPath is a prominent Robotic Process Automation (RPA) platform that allows businesses to automate repetitive, time-consuming tasks. By freeing up employees to focus on more value-added activities, UiPath can significantly improve operational efficiency and productivity.
- Minit: Minit is another popular process mining tool that provides organizations with a detailed view of their processes, enabling them to identify areas for optimization and implement process improvements.
- ARIS: ARIS (Architecture of Integrated Information Systems) is a comprehensive business process management (BPM) suite that helps organizations design, document, and analyze their processes. With its advanced modeling capabilities, ARIS enables businesses to create process maps, simulate changes, and identify opportunities for optimization.
- Nintex: Nintex is a process management and automation solution that enables organizations to create, manage, and optimize their workflows. With its wide range of features, including form creation, process mapping, and automation, Nintex helps businesses improve efficiency and productivity.
- Bizagi: Bizagi is a BPM suite that offers process modeling, automation, and analytics capabilities. It enables organizations to design, execute, and monitor their processes, driving continuous improvement and optimization.
- Bonita: Bonita is an open-source BPM and workflow automation platform that provides a range of tools for designing, executing, and monitoring business processes. With its customizable user interface and extensive integration options, Bonita can adapt to various business needs and requirements.
Process optimization examples
Optimizing business processes is a crucial step in the broader application of Business Process Automation (BPA). Let’s look at a few real-life examples of how business process optimization can increase efficiency in different parts of the organization.
1. Invoice approval
In many organizations, the invoice approval process is cumbersome and time-consuming. Invoices pile up as employees from different teams await manual approvals, leading to delays. To optimize this process, a company might deploy an automated invoicing system that could route invoices to the appropriate managers for approval automatically. The system can expedite the process, reduce errors, and ensure timely payments.
2. Sales order processing
Sales departments often encounter bottlenecks in order processing due to manual data entry and approvals. To optimize this process, a company can implement a system that automatically captures sales orders from multiple channels, validates customer information, and routes them for approval. By reducing manual intervention, the company may be able to speed up order processing, reduce errors, and improve customer satisfaction.
3. Customer support ticketing
Process optimization may be especially useful in customer support departments that often deal with high volumes of inquiries. To optimize this process, a company can introduce a ticketing system that automatically categorizes and routes customer inquiries to the appropriate department.
Challenges to process optimization
While process optimization can lead to improved efficiency and productivity, there are several challenges associated with it.
- Limited Resources. Process optimization requires resources, such as time and money. If resources are limited, it can be difficult to optimize a process.
- Reluctance to change. Change management is another challenge when optimizing a process. People are resistant to change, so it’s important to manage the process of change effectively.
- Leadership. In organizations process optimization requires a dedicated position of leadership to take charge of optimizing business processes.
- Inadequate training. Process optimization rarely works when the workflows and habits of key employees are changed without sufficient training.
- Unrealistic expectations. With process optimizations, it is not uncommon to have very lofty goals to achieve efficiency but many complex processes can not be improved in one big change.
Conclusion
Process optimization is a set of methods and tools used to make processes more efficient and effective. There are several types of process optimization techniques, including process mapping, process mining, and Six Sigma.
When optimizing a process, it’s important to identify goals, analyze current workflows, develop an optimized process, and test that optimized process. Challenges associated with process optimization include limited resources and change management.
ProcessMaker’s helps you discover all the existing processes in a seamless manner with the power of process intelligence, analyze them, and optimize using built-in automation capabilities.